Gitpod Self-Hosted Requirements
⚠️ Gitpod Self-hosted has been replaced with Gitpod Dedicated, a self-hosted, single-tenant managed service that runs in your private cloud account but is managed by us.
Try out Gitpod Dedicated.
Gitpod has certain expectations on the characteristics of the cluster it is running on as well as the (software) components connected to it.
Please refer to the product compatibility matrix for the supported types and versions of these components.
Cluster Requirements
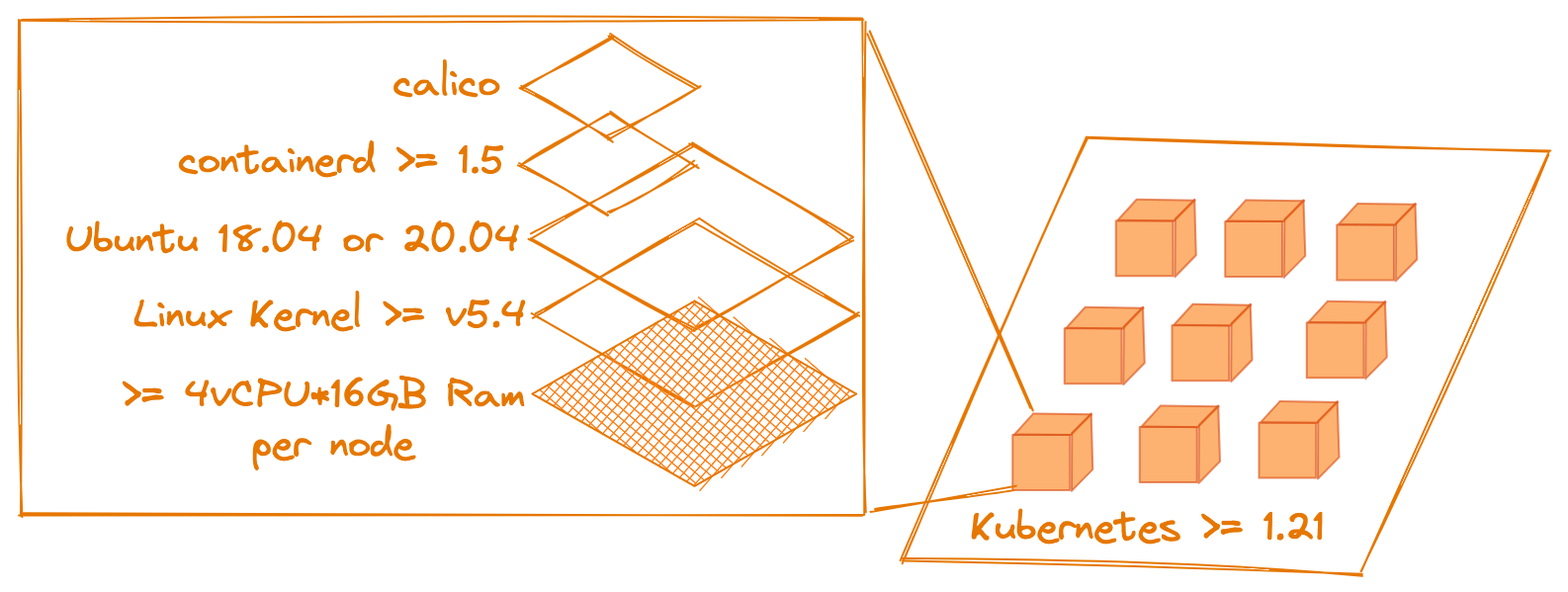
Reference Architectures
We have created a set of reference architectures for all the major cloud providers that fulfill the requirements below. These are intended as a starting point for you to create an environment to install Gitpod into. If you wish to use K3s, please refer to the k3s guide. Please see the product compatibility matrix for the current level of k3s support.
Supported Kubernetes Versions and distributions
Please refer to the product compatibility matrix for supported Kubernetes versions and distributions.
Node Affinity Labels Requirements
Your Kubernetes cluster must have node(s) with the following labels applied to them:
gitpod.io/workload_meta=truegitpod.io/workload_ide=truegitpod.io/workload_workspace_services=truegitpod.io/workload_workspace_regular=truegitpod.io/workload_workspace_headless=true
It is recommended to have a minimum of two node pools, grouping the meta and ide nodes into one node pool and workspace related nodes into another. These two groups of workloads have different performance characteristics. Separating them into node pools after the fact is more difficult and incurs downtime. A further improvement is to also separate the headless workspaces (these are prebuilds) and regular workspaces into separate node pools. Prebuilds can use up a lot of compute and this might impact regular workspaces if they are running on the same node.
Node and Container Requirements
These are the components expected on each node (see product compatibility matrix for supported versions):
- Ubuntu Linux
- Calico for the networking overlay and network policy
- Containerd
- At least 4 vCPU and 16GB of RAM
Kubernetes Privilege Requirements
Your Kubernetes cluster must allow Gitpod to run privileged pods, as Gitpod depends on these privileges to provide workspace isolation.
Load Balancer Requirements
Gitpod uses LoadBalancer type services to expose the Gitpod Dashboard, browser-based IDEs, and SSH connections used by desktop IDEs. Your Kubernetes cluster must be able to provision layer 4 or layer 7 load balancers for LoadBalancer type services that can route HTTP(S) connections to Gitpod services. If you intend to use desktop IDEs or SSH to workspaces then your cluster must also be able to provision layer 4 load balancers that can route SSH connection to Gitpod services.
All supported Kubernetes distributions provide load balancers that meet Gitpod’s needs. For more information see the Kubernetes distribution documentation below:
- Google Kubernetes Engine
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Engine:
- Layer 4/7 (default): Classic Load Balancer
- Layer 4 only: Network Load Balancing
- Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service
- K3s
Required Components
Gitpod relies on certain components and services for it to function. By default, most of these can be automatically installed in-cluster during installation. However, you can also configure Gitpod to use your own version of these that may or may not live inside the cluster. We recommend using external components when running Gitpod for sustained usage because this avoids the risk of data loss when the cluster goes down.
Please refer to the product compatibility matrix for the supported types and versions of these components.
| Component | Required? |
|---|---|
| Bucket Storage | Use default or bring your own |
| Database | Use default or bring your own |
| Image Registry | Use default or bring your own |
| Source Control Management System | Yes (cloud or self-hosted SCM) |
| Cert-manager | Yes |
Bucket Storage
By default, MinIO is installed in the cluster to store static content and to back an in-cluster image registry. During the installation process you can also configure Gitpod to use an external storage providers like S3.
Database
Gitpod uses a MySQL database to store user data. By default Gitpod ships with a MySQL database built-in and data is stored using a Kubernetes PersistentVolume. For production settings, we recommend operating your own MySQL database (version v5.7 or newer). Which database is used can be configured during installation.
Image Registry
Gitpod relies on an image registry to store images used to start workspaces. By default, a docker based image registry backed by MiniIO is installed in the cluster (this can be configured during the installation). However, Gitpod is also compatible with any registry that implements the Docker Registry HTTP API V2 specification.
Source Control Management System
Gitpod expects to be connected to a Source Control Management System (SCM) such as GitLab in order to function. You can find out more about which SCMs are supported and how to connect to them in the Integrations section. You will also be guided through connecting your SCM once you access your Gitpod installation for the first time.
Cert Manager
Cert-manager must be installed in your cluster before you can install Gitpod. It is used to create and manage certificates needed to secure communication between the various internal Gitpod components. It can also be used to fetch a TLS certificate for your Gitpod instance from Let’s Encrypt for example. Please consider the cert-manager documentation on how to install it.