Setting up your EKS cluster with dual ALB + NLB load balancers
⚠️ Gitpod Self-hosted has been replaced with Gitpod Dedicated, a self-hosted, single-tenant managed service that runs in your private cloud account but is managed by us.
Try out Gitpod Dedicated.
If you are unable to use an AWS classic load balancer (CLB) (e.g. because you want to use SSL Certificates generated by AWS) you need to set up an Application Load Balancer (ALB) for HTTPS traffic (e.g. when using VS Code in the browser). If you wish to use Desktop IDEs together with Gitpod Self-Hosted, which use SSH for networking, and thus require a Level 4 load balancer, you also need to create a Network Load balancer (NLB) (which is a Level 4 load balancer that can handle ssh traffic). AWS’ ALB is a level 7 load balancer and can only handle HTTPS traffic.
This guide shows how to install both an ALB and an NLB into an EKS cluster. It is meant to be used as a supplement to the Single Cluster Reference Architecture (AWS) which only installs a CLB by default. You will configure your DNS to point ssh traffic to the NLB and HTTPS traffic to the ALB.
Note: This guide assumes that you will be using AWS to manage your SSL certificates.
Setting up an ALB and NLB
0. Node configuration
Because we need to use an internal CA for communication that has to be distributed to the nodes, we need to ensure all managed nodes have /etc/containerd/certs.d in their /etc/containerd/config.toml to load the self-signed certificate used for internal communication.
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry]
config_path = "/etc/containerd/certs.d"These are two examples to enforce this:
- Use python to insert the values into the toml file respecting the formatting:
apt-get update && apt-get install -y python3-pip
pip3 install toml mergedeep
/usr/bin/env python3 - << EOF > /var/log/update-containerd-config-out.txt 2>&1
import toml
from mergedeep import merge
c = toml.load('/etc/containerd/config.toml')
merge(c, {'plugins': {'io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri': {'registry': {'config_path': '/etc/containerd/certs.d'}}}})
with open('/etc/containerd/config.toml', 'w') as f:
toml.dump(c, f)
EOF
service containerd restart- Bruteforce method that will just append the lines to
/etc/containerd/config.tomlwhich will work if there are no other registry settings present in your config.toml file
cat << CONFIG >> /etc/containerd/config.toml
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry]
config_path = "/etc/containerd/certs.d"
CONFIG
service containerd restartExample of a complete overridebootstrap command
overrideBootstrapCommand: |
#!/bin/bash
set -x
export CLUSTERNAME=gitpod
export NODEGROUP=services
export CONTAINER_RUNTIME=containerd
declare -a LABELS=(
eks.amazonaws.com/nodegroup="${NODEGROUP}"
gitpod.io/workload_meta=true
gitpod.io/workload_ide=true
)
export USE_MAX_PODS=false
export KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="$(printf -- "--node-labels=%s" $(IFS=$','; echo "${LABELS[*]}"))"
/etc/eks/bootstrap.sh ${CLUSTERNAME} --use-max-pods false
# Update containerd config while waiting on https://github.com/gitpod-io/gitpod/issues/11005
apt-get update && apt-get install -y python3-pip
pip3 install toml mergedeep
/usr/bin/env python3 - << EOF > /var/log/update-containerd-config-out.txt 2>&1
import toml
from mergedeep import merge
c = toml.load('/etc/containerd/config.toml')
merge(c, {'plugins': {'io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri': {'registry': {'config_path': '/etc/containerd/certs.d'}}}})
with open('/etc/containerd/config.toml', 'w') as f:
toml.dump(c, f)
EOF
service containerd restart1. Install AWS load balancer controller
Install the AWS load balancer controller. The below example assumes you have created the user aws-load-balancer-controller with the correct IAM permissions already. --set hostNetwork=true is required by Calico.
helm repo add eks https://aws.github.io/eks-charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade aws-load-balancer-controller \
eks/aws-load-balancer-controller \
--atomic \
--cleanup-on-fail \
--install \
--reset-values \
--namespace kube-system \
--set clusterName=<insert cluster name> \
--set serviceAccount.create=false \
--set serviceAccount.name=aws-load-balancer-controller \
--set hostNetwork=true2. Install Gitpod
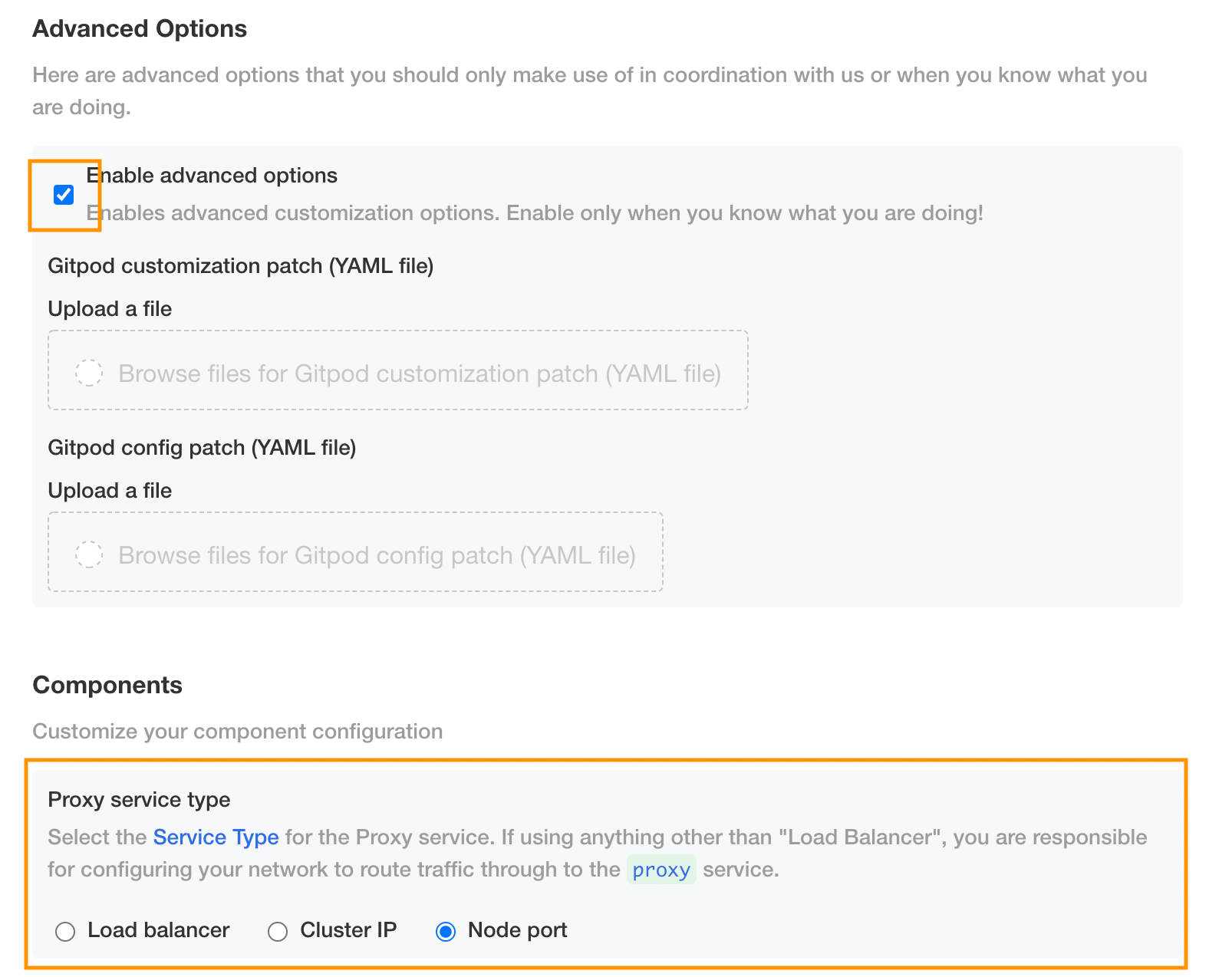
Ensure that you’ve created all the required components as per the reference architecture guide: Object Storage, OCI Image Registry, Database. Then install Gitpod. While configuring your Gitpod installation, make sure to check ‘use self-signed certificate’. Make sure that you select node port as the service type for the proxy service in the components section of the installation UI (this assumes you are using version 2022.07 or later):
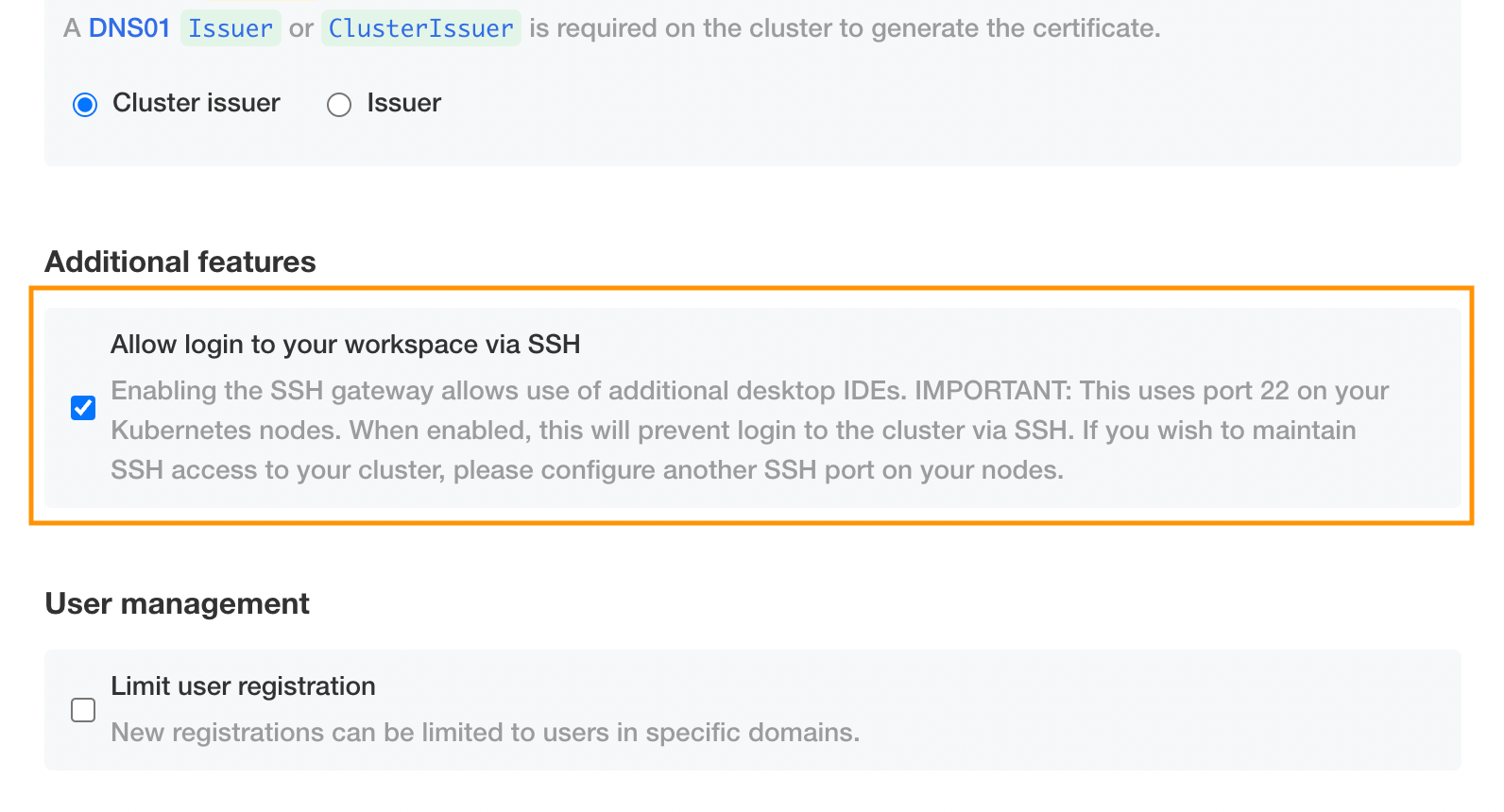
You will also need to make sure that the “allow login via SSH” box is ticked:
3. Create alb-ingresss.yaml
Update the alb-ingress.yaml below with your site-specific options (you need to customize anything tagged with <..>):
alb-ingress.yaml
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.ssl-redirect: |-
{
"Type": "redirect",
"RedirectConfig": {
"Protocol": "HTTPS",
"Port": "443",
"StatusCode": "HTTP_301"
}
}
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: HTTPS
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: |-
[{
"HTTP": 80
}, {
"HTTPS": 443
}]
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-attributes: idle_timeout.timeout_seconds=3600
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/tags: Purpose=Gitpod,Service=proxy
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes: deregistration_delay.timeout_seconds=30
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-node-labels: gitpod.io/workload_meta=true
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: instance
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-policy: ELBSecurityPolicy-FS-1-2-Res-2020-10
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: <YOUR-AWS-SSL-PROVIDED_CERTIFICATE>
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: <SET THIS -> internet-facing or internal>
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-name: <GITPOD-LOAD-BALANCER-NAME>
name: gitpod
spec:
defaultBackend:
service:
name: proxy
port:
number: 80
rules:
- http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: proxy
port:
number: 443
path: /
pathType: Prefix4. Install ALB and NLB
Install the ALB (for HTTPS traffic) and NLB (for SSH traffic) using the .yaml file customized above as well as this one:
nlb-ssh-service.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: gitpod-ssh
labels:
app: gitpod
component: ws-proxy-ssh
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-name: gitpod-ssh-gateway
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: external
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: 'instance'
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ip-address-type: ipv4
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol: tcp
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-target-node-labels: gitpod.io/workload_workspace_services=true
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-target-group-attributes: stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.type=source_ip,preserve_client_ip.enabled=true
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-additional-resource-tags: Project=gitpod-alb
spec:
ports:
- name: ssh
protocol: TCP
port: 22
targetPort: 2200
selector:
app: gitpod
component: ws-proxy
type: LoadBalancerkubectl apply -f alb-ingress.yaml
kubectl apply -f nlb-ssh-service.yaml5. Check if installed properly
If installed properly, then this should be the shell output given the command below:
> kubectl get ingress gitpod -n gitpod
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
gitpod <none> * gitpod-airgap-alb-339697413.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80 41s
> kubectl get service gitpod-ssh -n gitpod
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
gitpod-ssh LoadBalancer 172.20.162.102 gitpod-ssh-gateway-6588d186387780e5.elb.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com 22:30003/TCP 76s6. Update DNS records
Update DNS as follows to point to your newly created loadbalancers depending on the type of traffic:
gitpod.domain.com --> ALB ADDRESS
*.gitpod.domain.com --> ALB ADDRESS
*.ssh.ws.gitpod.domain.com --> NLB ADDRESS